
PPT Clinical Enzymology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
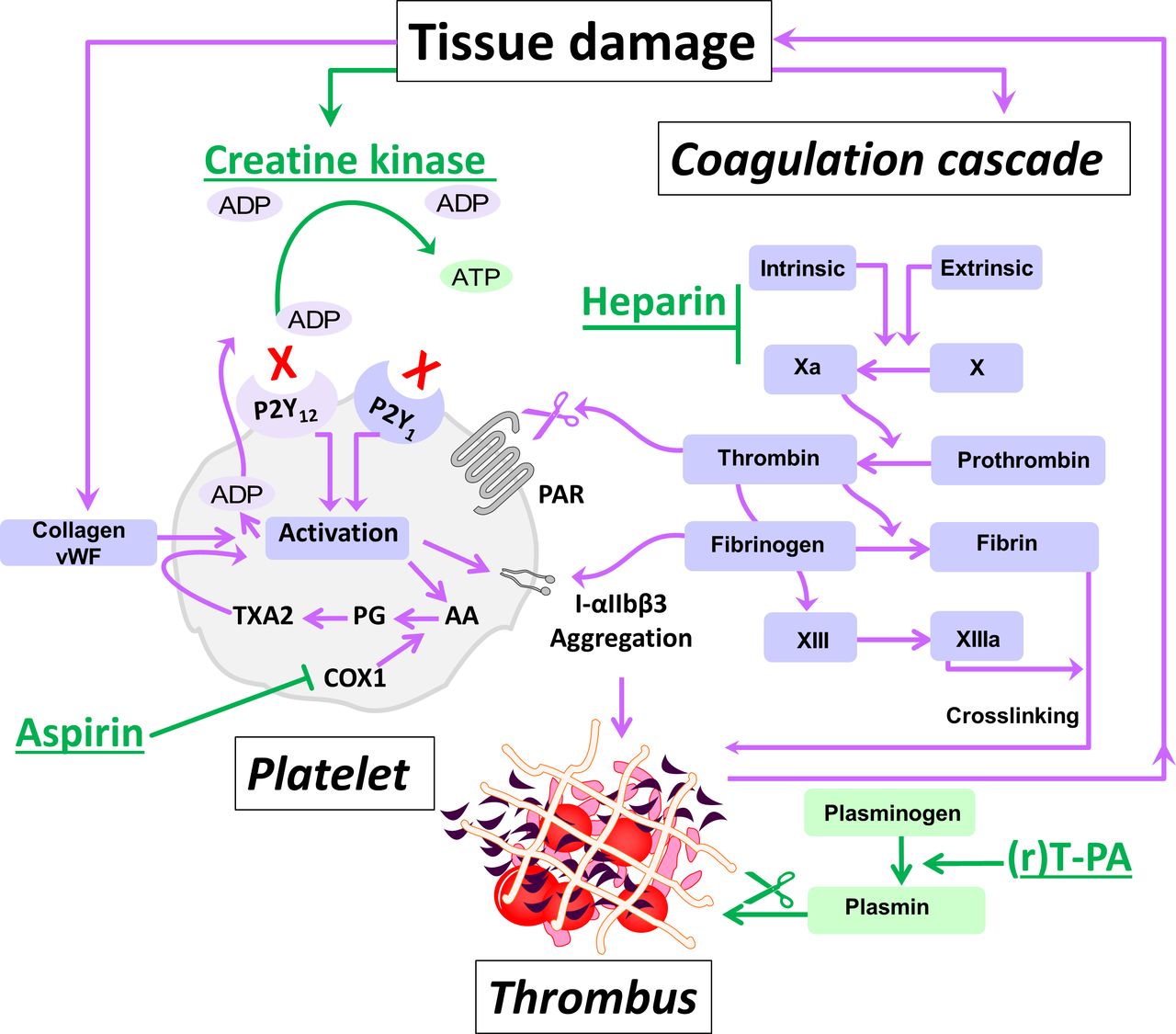
Creatine kinase (known previously as creatine phosphokinase or CPK) is distinct from creatinine and is a biomarker of muscle damage. The reference range for normal creatine kinase is 40‐320 IU/L for men and 25‐200 IU/L for women, though this may vary across laboratories and assays. Creatine kinase levels are dependent on age, sex, and.

Creatine vs Creatinine Difference and Comparison
Main Difference - Creatine vs Creatinine. Creatine and creatine are two protein derived compounds found in the animal body. Creatine is produced in the liver, kidney, and pancreas and transported into skeletal muscles through the blood.. "Creatine kinase rxn" By Boghog2 - Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia 2.

CK (Creatine Kinase) Is Associated With Cardiovascular Hemodynamics
Creatine Kinase vs Creatinine Blood Test. The Creatine kinase test diagnoses chronic or acute skeletal muscle, heart, or brain damage or degeneration. Creatinine blood tests diagnose kidney problems, especially diabetic nephropathy or diabetic kidney disease. Creatine kinase (CK) is an enzyme that works as a catalyst during the rapid.

PPT Creatine and Creatinine PowerPoint Presentation, free download
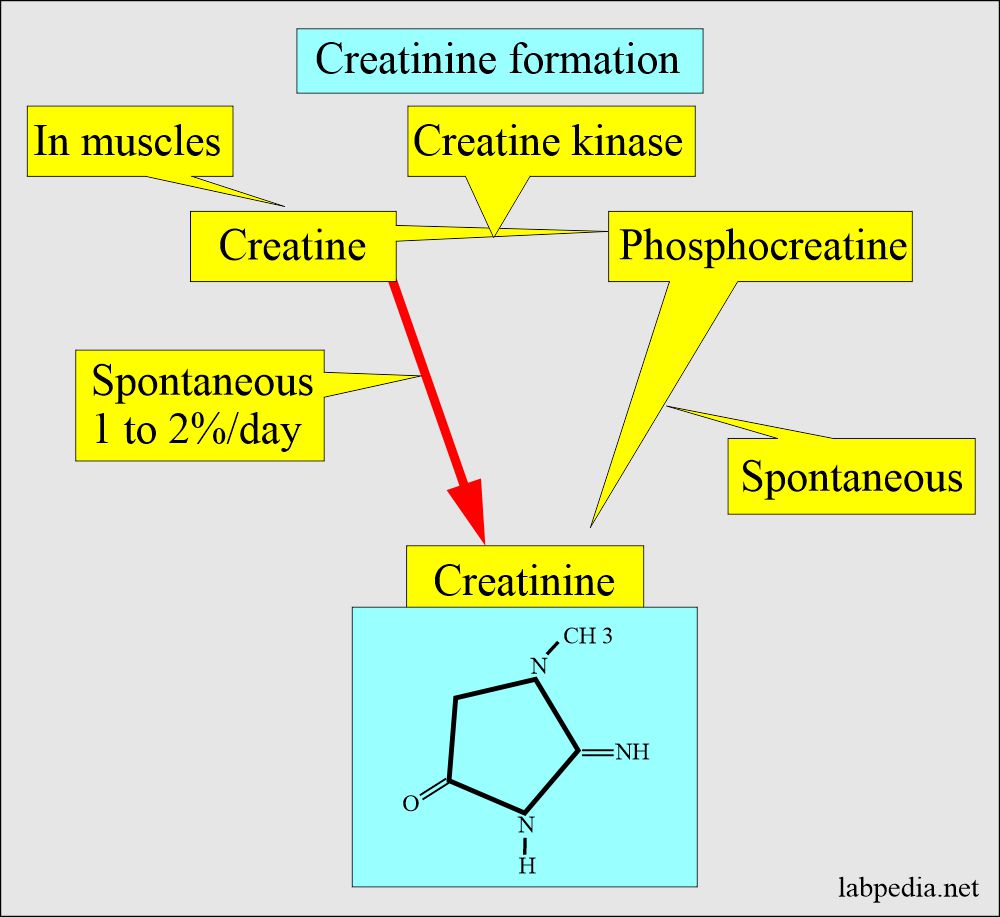
Rather than creatinine kinase, presumably the authors were instead referring to the enzyme creatine kinase. Creatine kinase catalyses the phosphorylation of creatine to phosphocreatine, is frequently measured as a marker of muscle damage, and is commonly abbreviated as "CK" . Creatinine is neither a product nor substrate for creatine kinase.
Creatinine (Serum Creatinine)
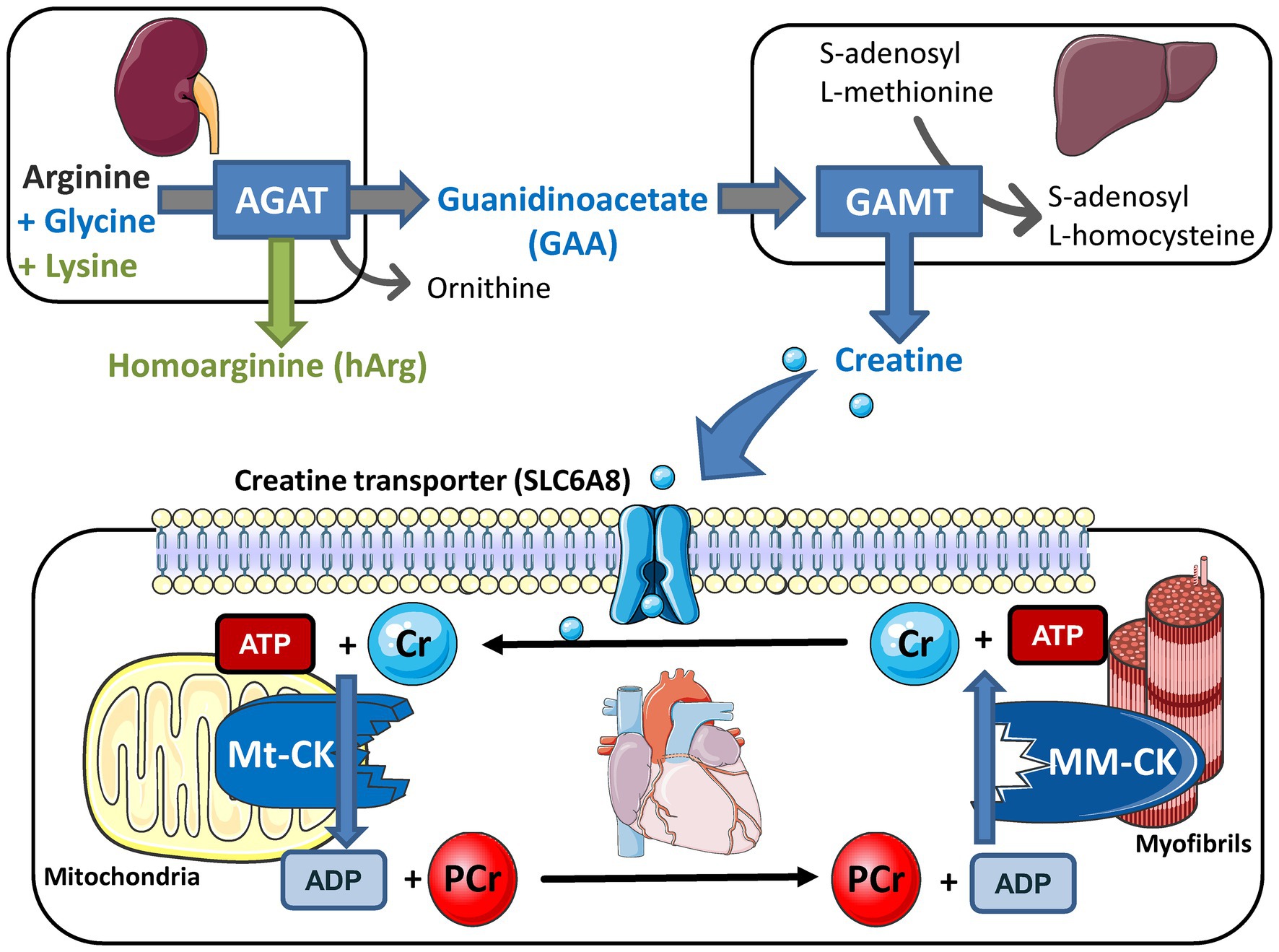
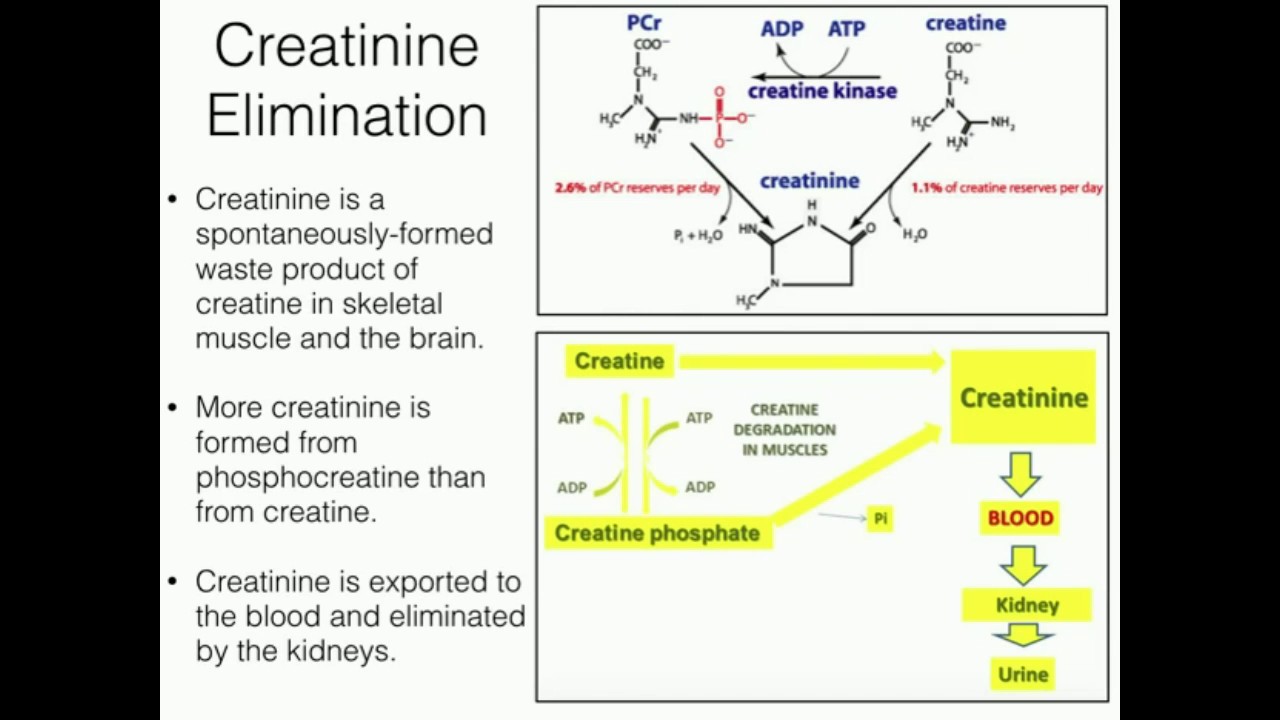
Creatine is converted to phosphocreatine (PCr), regulated by the enzyme creatine kinase (CK) in muscle and used to create intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In reality, transient increases in blood or urinary creatine or creatinine due to creatine supplementation are unlikely to reflect a decrease in kidney function. Additionally.

PPT Creatine and Creatinine PowerPoint Presentation, free download
It is commonly seen in trauma and electrical burns patients. To prevent morbidity and mortality from ARF due to rhabdomyolysis, early detection of ARF by monitoring the biochemical parameters such as serum creatinine, serum creatine kinase (CK), and urinary myoglobin (UM) can be helpful . We performed this study in trauma and electrical burns.
Creatine Kinase
Creatine versus Creatinine. You could call it hair-splitting, but it seems a small mistake has. occured concerning the nomenclature of the enzyme 'creatine kinase' (EC. 2.7.3.2): several times the enzyme was called 'creatinine kinase'. The. enzyme creatine kinase catalyzes the formation of phosphocreatine from ATP.
Creatine kinase is associated with bleeding after myocardial infarction
Creatine kinase (CK), also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) or phosphocreatine kinase, is an enzyme (EC 2.7.3.2) expressed by various tissues and cell types.CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and uses adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to create phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). This CK enzyme reaction is reversible and thus ATP can be generated from PCr and ADP.
Kreatin kinaz Tıpacı
Blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine, for renal function and evidence of acute kidney injury (AKI). Creatine kinase elevation — Serum CK levels at presentation of rhabdomyolysis are usually at least five times the upper limit of normal, but range from approximately 1500 to over 100,000 units/L.

Determination of Serum Creatinine KendaloiPatterson
The main difference between creatinine and creatine kinase is that creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism whereas creatine kinase is the enzyme that converts creatine into creatine phosphate. In general, creatinine and creatine kinase are two related objects to creatine, which is an organic.
Creatine Function (2/2) Degradation to Creatinine YouTube
CK-MB test. The CK-MB test is a blood test that looks for a specific enzyme. That enzyme, creatine kinase-myocardial band, is most common in your heart but can also mean you have damage to other muscles in your body. The use of this test has decreased because of newer tests that have a better ability to detect heart damage only.
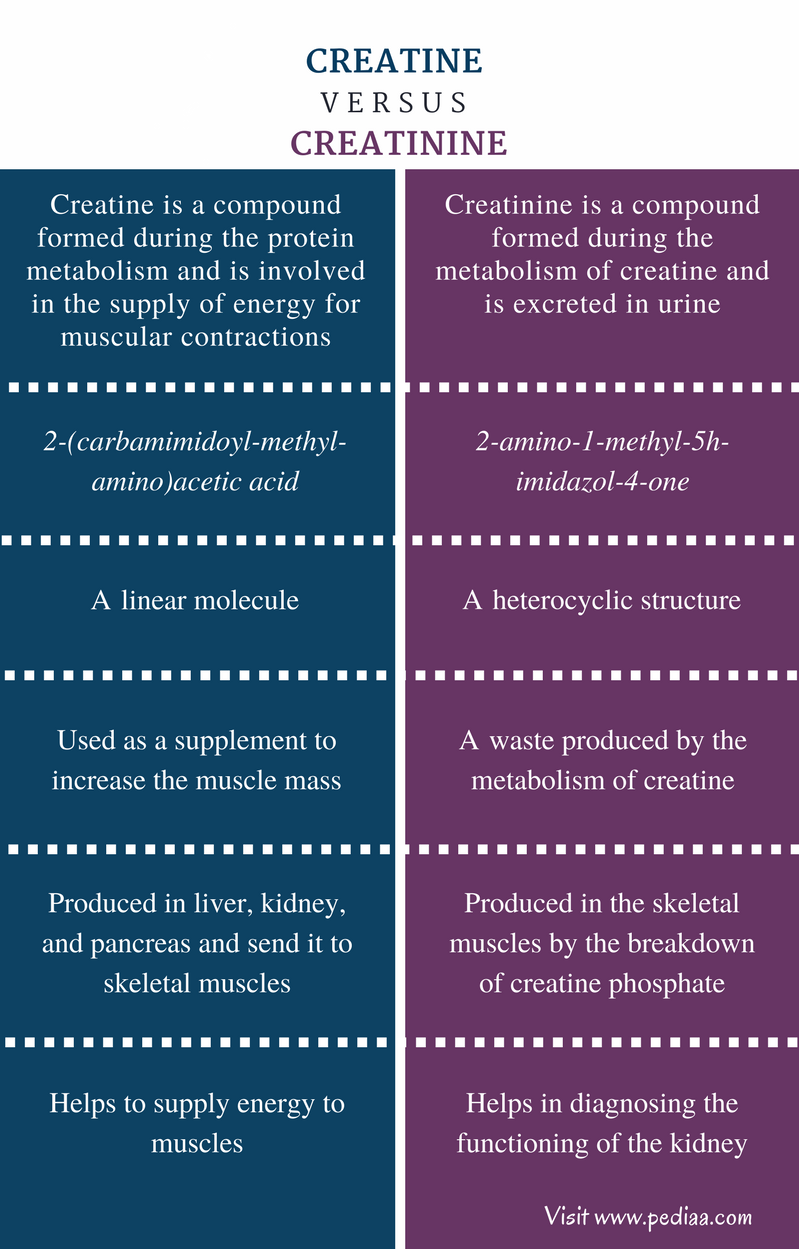
Difference Between Creatine and Creatinine Definition, Features
Summary. The creatine kinase test is a blood test that checks whether the CK levels in your blood are elevated. Elevated CK levels can mean you have some sort of muscle damage in your body. It doesn't provide a full picture of your health, so healthcare providers typically perform other tests to make a diagnosis.

Creatine vs Creatinine Difference and Comparison
Creatinine vs creatine kinase. A 46-year-old member asked: Creatine kinase vs creatinine, is there a difference between them? Dr. Bennett Werner answered. Cardiology 46 years experience. Yes: Creatine kinase is a muscle enzyme that is measured to assess heart damage (the mb isoenzyme form) or skeletal muscle damage (the mm isoenzyme). Creat.

PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation ID6198545
Creatinine Kinase. Creatine kinase (CK) is primarily cytosolic, and four major isoenzymes have been reported with variable distribution: CK-1 predominates in brain; CK-2 and CK-3 in cardiac and skeletal muscle; and CK-Mt in mitochondria of various tissues. CK activity in serum samples from healthy dogs may be higher than in plasma samples, the.
Creatine kinase (CK), Creatine phosphokinase (CPK)
Creatinine clearance is a measure of how well the kidneys filter creatinine out of the bloodstream for excretion in urine. Creatinine clearance is usually determined from a measurement of creatinine in a 24-hour urine sample and from a serum sample taken during the same time period. However, shorter time periods for urine samples may be used.
Simply Stated The Creatine Kinase Test Quest Muscular Dystrophy
Creatine kinase (CK), formerly known as creatine phosphokinase, is an intracellular enzyme present in greatest amounts in skeletal muscle, myocardium, and brain; smaller amounts occur in other visceral tissues. Disruption of cell membranes due to hypoxia or other injury releases CK from the cellular cytosol into the systemic circulation.